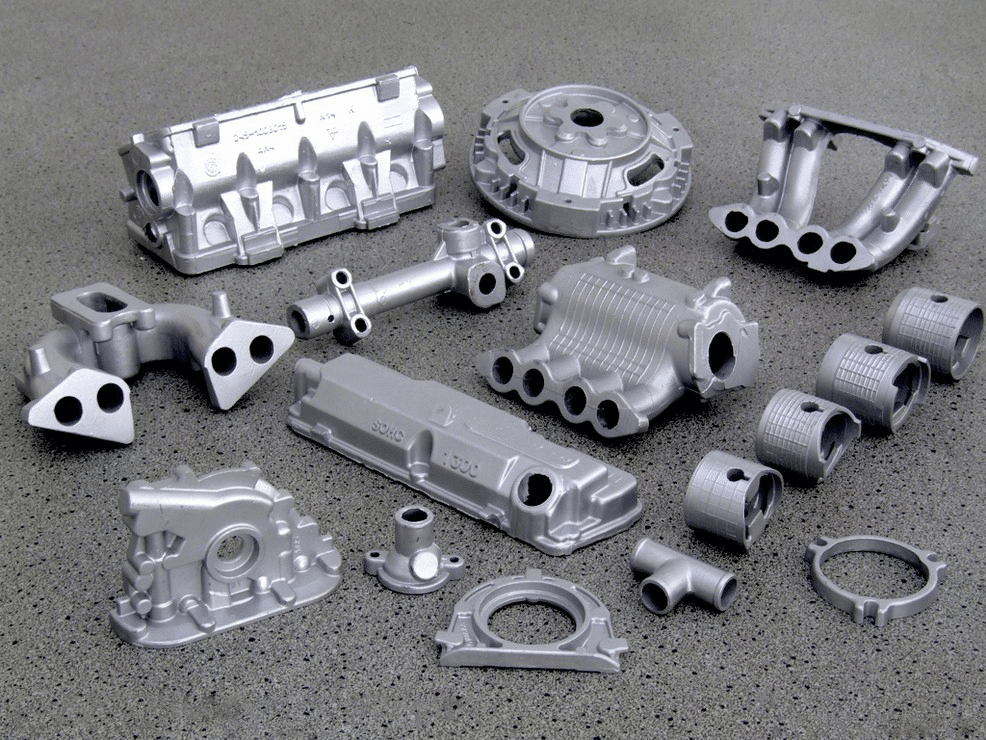
How is die casting done?
Currently, the parts manufactured by using the method of die casting are used for the production of aircraft, machine tools, heavy machinery, and passenger cars. Besides, this technology is closely related to the production of LED lighting as it can be used to manufacture housings and cooling radiators.
Process description
This technology allows you to produce parts from a range of metals and alloys. For example, aluminium die casting has a wide scope of application. Steel moulds, whose forming cavities correspond to the geometry of the outer surface of a final product, are used during this process. The moulding unit contains ejectors, designed to extract a half-finished product, and movable metal rods to create internal cavities.
This technology consists of several stages:
- opening and lubricating a mould to facilitate the removal of a half-finished product and the formation of a thin protective film that helps stabilize the temperature and protect the surface of the tooling, thereby extending its service life;
- closing the mould;
- drawing an optimal amount of molten metal and pouring it into the piston bore;
- pressing material;
- taking out the final product.
In some cases, when it is required to achieve high strength characteristics, the material is poured into the tooling in the half-solid, half-liquid state. The final product is shaped without shrinkage defects and is not welded to the tooling.
Characteristic features
Products manufactured by using this technology have the following advantages:
- low roughness;
- high precision performance;
- no need for any further machining (in most cases).
Besides, die casting technology can be fully automated. Thanks to the high rate of solidification of products, it is possible to achieve high performance. However, this technology has some drawbacks:
- inability to manufacture products from refractory metals;
- high cost of the tooling.
In addition to that, this technology is unsuitable for small-scale production.