Advantages and disadvantages of die casting
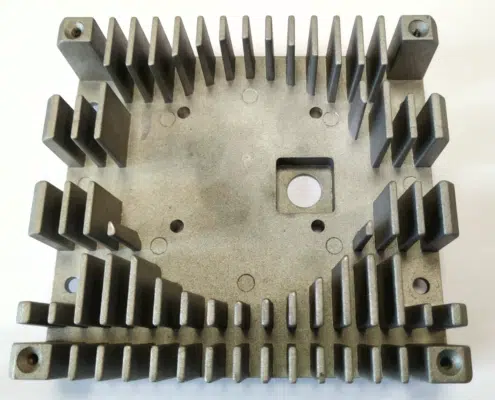
Metal die casting – is a production technology of castings, in which the alloy under pressure up to 700 MPa quickly fills the mold. Products made in this way can be of different sizes and have weigh up to several kilograms. As a basic raw material normally are used following: non-ferrous metals — copper, aluminum, and their alloys.
Die casting makes it possible to obtain high-precision products (along with such technology as powder metallurgy, which allows to obtain sintered metal parts that are particularly hard and wear-resistant).
USEFUL INFORMATION FOR CUSTOMERS
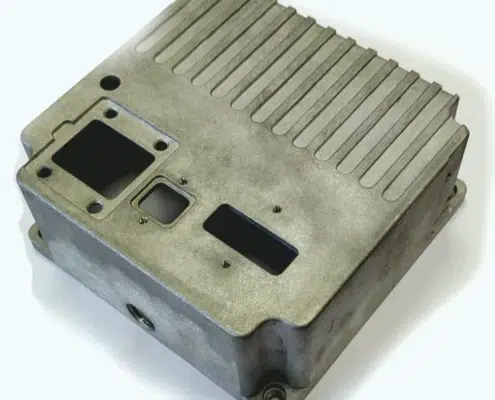
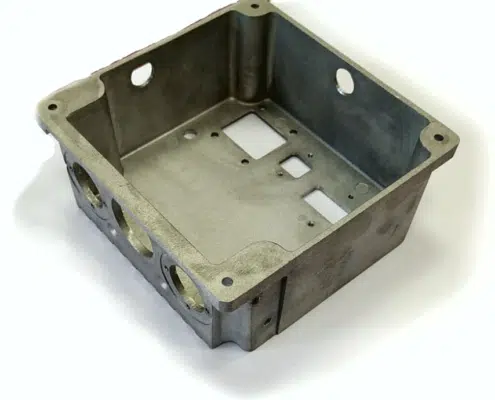
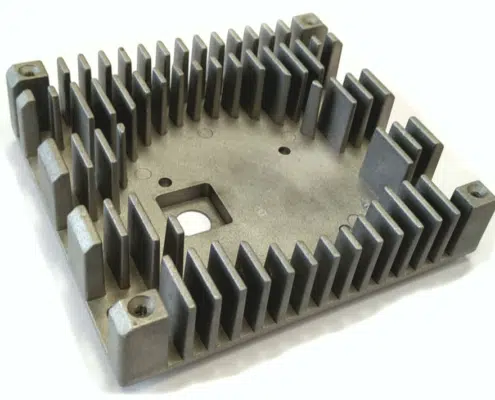
Our company specializes in the fabrication of components for LED illumination and other premium-grade castings. A notable advantage inherent in die casting lies in the innate resistance of the final products to corrosion. This phenomenon arises from the formation of a robust surface crust during the manufacturing process, characterized by a dense composition and minimal moisture permeability.
Die casting, while relatively rapid, unfolds across several intricate stages encompassing mold preparation, raw material melting, molten metal pouring, and subsequent compression. The resultant castings boast a smooth surface texture, obviating the need for post-casting machining due to their low roughness. Employing die casting technology permits the utilization of multi-cavity molds and facilitates the creation of components featuring delicate, slender walls, such as carburetor diffusers. This methodology yields castings characterized by pronounced, well-defined contours, achieving precision levels within the 3-7 classification range.
Conversely, a primary drawback associated with die casting pertains to the potential occurrence of vortex formation during the molten metal pouring phase, leading to air entrapment within the material. However, meticulous oversight from our skilled specialists effectively mitigates this issue, minimizing its occurrence to virtually negligible levels.